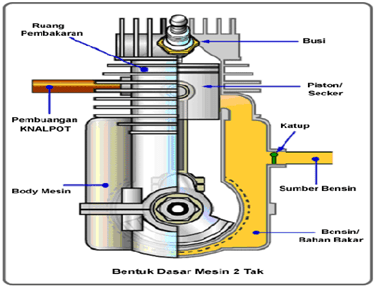
In the emergence of an internal combustion engine, a 2 stroke (two stroke) engine is one of the simplest engines. Only a few moving parts, including the crankshaft, piston, and several others. Where, the 2 stroke engine does not use a valve (valve) and noken as (camshaft) as in the 4 stroke engine, instead the engine 2 does not use a membrane that is after the carburetor. These advantages make the 2-stroke engine lighter, simpler and cheaper to produce.
2-stroke engine is one type of engine on the automotive world market. As its development, this machine was abandoned and rarely produced by large manufacturers of automotive vendors due to the exhaust emissions are quite large. In addition, this type of salt is very wasteful in fuel consumption compared to other types of engines so that we rarely encounter and even no motorcycles and cars use this engine.
In addition, because the 2-stroke engine in one rotation of the crankshaft carries out 4 cycles, namely: suction, compression, expansion and exhaust. This 2 stroke engine is more responsive and has good acceleration. However, this engine emits more power when the RPM is high so that this engine consumes more fuel. The combination of light and twice the power gives this 2 stroke engine the power-to-weight ratio is greater when compared to the 4 stroke engine.
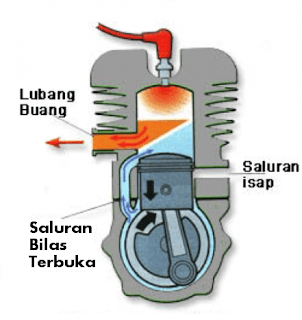
- Suction and Compression steps
When the piston moves from the lower dead point (TMB) to the upper dead point (TDC), the space under the piston will be vacuum, as a result a mixture of fuel, air and oil is sucked into the chamber. While in the upper chamber of the piston compression steps occur so that the temperature and pressure of the mixture of air and fuel increases. When it is 5-10 degrees before TDC, the spark plug produces sparks so that the mixture of fuel and air whose temperature and pressure have risen will catch fire and explode.
- Expansion and Discard Steps
The result of this combustion makes the piston move downward. When the piston is pushed down and down, the space under the piston becomes compressed. So that the mixture of air and fuel in the piston chamber is pushed out and up to the chamber above the piston through the rinse channel. While the rest of the combustion results will be pushed out of the combustion chamber and out into the exhaust and then to the exhaust. When the mixture of fuel and air pushes away the combustion gases, there must be a mixture of the fuel carried into the exhaust.
With a 2 stroke engine muffler, the fuel mixture can be kicked back into the combustion chamber because the bubbling exhaust will increase in pressure and this pressure will kick back the fuel mixture. The hot combustion gases also enter the combustion chamber a little, which helps increase the temperature of the new fuel mixture into the combustion chamber and will cause the fuel mixture to combust easily. This work step occurs repeatedly during the engine’s life.